

Auto-fluorescence based technology : Dental calculus contains various kinds of non-metallic and metallic based components.

Irrespective of its effectiveness in the detection of dental calculus, this process is not widely used due to its high cost and the amount of extensive training required before successful usage. The images it captures can be viewed in real-time on a computer screen and also recorded for further usage for research, training, and treatment. A Perioscope is generally composed of fiber-optic bundles bound by multiple illumination fibers, an irrigation system, and a light source. After the device is inserted into the periodontal pocket, a Perioscope is used for the screening of subgingival root surface, tooth surface, and calculus. We were introduced to this procedure in the year 2000, which involved using a miniature periodontal endoscope.

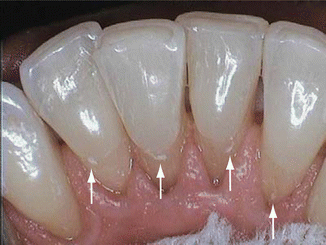
The use of near-ultraviolet (NUV) and near-infrared lasers are one of those methods. There are potentially more effective methods for the dental calculus removal procedure. The most satisfactory results in dental debridement are achieved when using ultrasonic tools in adjunct to hand instrumentation. Moreover, it is used for root planning, curettage, and surgical debridement. Ultrasonic scalers are more effective in removing the calculus layer, stain, and plaque. Hoes, chisels, and files are less widely used as they are beneficial for removing large amounts of calculus. These devices are designed to meet specific needs for different parts of the mouth.Īn ultrasonic device is also used to incorporate a combination of high-frequency vibrations with water to extract the tartar. To achieve the most effective calculus teeth removal, an oral hygienist will use hand-held dental tools like a periodontal scalar, curettes, hoes, files, and chisels. An integral part of being a dental hygienist is getting familiar with the process of plaque and calculus removal, which is famous as debridement. Plaque and calculus deposits are a significant factor in the formation and progression of dental diseases. The plaque layer is mostly seen at both the teeth surface, gum line (known as supragingival), and also in the narrow gap (sulcus) between the gum and the teeth (known as subgingival). Although a mild dental procedure kills the bacteria and leaves a rough and hardened surface, which is more susceptible to further growth of plaque and tartar. This layer of deposition eventually hardens to form a tartar layer. The calculus or the tartar layer is a result of the constant deposition of saliva, Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF) and other bacterial deposits over the surface of the teeth.
#SUBGINGIVAL CALCULUS REMOVAL PROFESSIONAL#
In that case, one has to take professional help where it can be removed with ultrasonic tools or designated dental tools such as a periodontal scalar. Once formed, calculus is too hard and attached to remove with regular brushing and flossing. Successful treatment also protects the tissues that are surrounded and supported by the teeth (known as periodontium). An effective calculus tartar treatment significantly reduces the number of bacteria present in the mouth, which also hinders the further growth of bacteria. Dental calculus removal often requires the patient to be anesthetized depending on the seriousness of the dental condition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
